Assignment 2
Assignment 6. Please review the course web site for access dates: Click on the begin button to access the assignment and submit your answers. This covers Unit VI Earth’s Dynamic Atmosphere in the textbook (Chapters 11, 12, 13, and 14).
Elevate Your Writing with Our Free Writing Tools!
Did you know that we provide a free essay and speech generator, plagiarism checker, summarizer, paraphraser, and other writing tools for free?
Access Free Writing ToolsMULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. (1 point each)
1) The annual temperature range at most latitudes in the Southern Hemisphere is much smaller than that in the Northern Hemisphere. The reason for this is that ________.
A) rainfall and cloudiness are greater in the Southern Hemisphere
B) Earth is closest to the Sun during the Southern Hemisphere summer
C) there is a greater percentage of water surface in the Southern Hemisphere
D) a greater proportion of the land surface is mountainous in the Southern Hemisphere
Answer; C) there is a greater percentage of water surface in the Southern Hemisphere
2) Imagine you are in a flying aircraft. You note the presence of clouds and storms at your same altitude. What layer of the atmosphere must the aircraft be traveling through?
A) stratosphere B) troposphere C) mesosphere D) ionosphere
Answer; B) troposphere
3) Dust in the atmosphere is responsible for which of the following?
A) optical phenomena such as a red sky at sunset
B) reflection of solar energy
C) acting as a nucleus for condensation and cloud formation
D) Atmospheric dust does all of these.
Answer; D) Atmospheric dust does all of these.
4) Water vapor levels in Earth’s atmosphere ________.
A) range between 0% and 4%
B) vary from place to place and time to time
C) are a major mechanism of transport of latent heat
D) all of the above
Answer; D) all of the above
5) Which of the following can influence temperature?
A) position on a landmass B) cloud cover
C) altitude D) all of the above
Answer; D) all of the above
6) Which one of the following is the most abundant gas in the atmosphere?
A) nitrogen B) ozone C) carbon dioxide D) oxygen
Answer; A) nitrogen
7) The term ________ is used to describe the conversion of a solid directly to a gas, without passing through the liquid state.
A) sublimation B) melting C) condensation D) evaporation
Answer; A) sublimation
8) Rising air is ________ air.
A) stable B) cloudy C) warming D) unstable
Answer; D) unstable
9) Why are hygroscopic nuclei important?
A) They aid in evaporation, and therefore in cloud dissipation.
B) They encourage cooling of the atmosphere.
C) They facilitate warming of the atmosphere.
D) They aid in condensation, and therefore in cloud formation.
Answer; D) They aid in condensation, and therefore in cloud formation.
10) Clouds consist of ________.
A) water droplets B) white-colored gases
C) ice particles D) either water droplets or ice particles
Answer; D) either water droplets or ice particles
11) When warm moist air moves over a cold surface, ________ fog may result.
A) upslope B) steam C) radiation D) advection
Answer; D) advection
12) How can condensation be triggered to form clouds or fog?
A) Cool the air to its dew point.
B) Add sufficient water vapor to the air so that it reaches saturation.
C) Either of the above will work.
D) Neither of the above will work.
Answer; A) Cool the air to its dew point.
13) What two kinds of fog are the result of adding moisture to a layer of air?
A) radiation and upslope B) advection and radiation
C) steam and frontal D) upslope and steam
Answer; C) steam and frontal
14) The Sahara and Australian deserts (among others) are associated with the ________.
A) anticyclone B) subpolar low C) subtropical high D) equatorial low
Answer; C) subtropical high
15) The zone of subsiding dry air which encircles the globe near 30° latitude, north and south, is known as the ________.
A) subtropical high B) Hadley cell C) polar front D) trade winds
Answer; A) subtropical high
16) When the pressure gradient force is balanced by the Coriolis force, high altitude ________ move parallel to isobars.
A) geostrophic winds B) monsoons C) valley breezes D) chinooks
Answer; A) geostrophic winds
17) Which of these factors influence the magnitude of the Coriolis Effect (force)?
A) wind speed B) wind direction
C) latitude D) both wind speed and latitude
Answer; D) both wind speed and latitude
18) Examine the map showing air pressure in millibars. Which of the four lettered locations deserves a wind hazard alert?
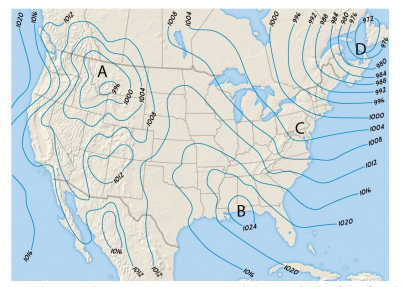
A) A B) B C) C D) D
Answer; B) B
19) Because unequal heating of Earth’s surface generates these pressure differences, ________ is/are the ultimate energy source for most wind.
A) solar radiation B) hot springs
C) the greenhouse effect D) caves
Answer; A) solar radiation
20) Examine the figure. Which of the four lettered columns shows the correct order of slowest wind symbols (top) to fastest wind symbols (bottom)?
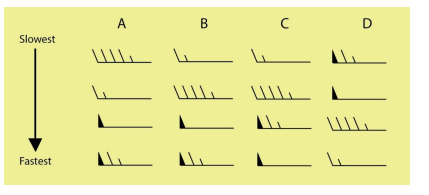
A) A B) B C) C D) D
Answer; B) B
21) A cyclone is ________.
A) another name for the low-pressure systems that take several days to travel across North America from west to east
B) the term for circulation around any low-pressure center, no matter how large or intense it is
C) another name for a tornado
D) another name for a hurricane
Answer; B) the term for circulation around any low-pressure center, no matter how large or intense it is
22) On a weather map, ________ are shown by a line with triangular points on one side.
A) dragon mouths B) occluded fronts C) warm fronts D) cold fronts
Answer; D) cold fronts
23) Examine the figure. Which of the symbols shown is used to illustrate a stationary front?
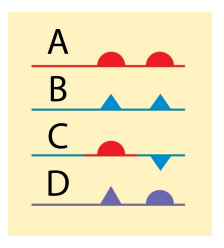
A) A B) B C) C D) D
Answer; C) C
24) An air mass originating in the Gulf of Mexico should be labeled ________.
A) mT B) cP C) cT D) mP
Answer; A) mT
25) Should people be more concerned about tornado warnings or tornado watches?
A) tornado watches B) tornado warnings
C) both mean the same thing D) neither are of concern
Answer; B) tornado warnings
Explore psychology questions with multiple answers.
Fill in the blank. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. (1 point each)
26) Relative to lower temperatures, high temperatures require ________ (more / the same amount / less) moisture to fully saturate the air.
27) Mixing ratio, relative humidity, and dew-point temperature are all ways of measuring the amount of ________ in the air. Answer; water vapor
28) Examine the photo. These balloons are rising because the ________ air inside the balloon is less dense than the surrounding air.

Answer; hot warm
29) ________ occurs when warm air is forced up and over a mass of cooler air. Answer; frontal wedging
30) ________ is a cloud with its base at or very near the ground. Answer; fog
31) Updrafts in cumulonimbus clouds may loft small particles of ice through the cloud, coating them and producing ________. Answer; hail
32) ________ is the result of horizontal differences in air pressure. Answer; wind
33) For a low-pressure center to be maintained or strengthened, the surface convergence must be balanced by ________ aloft. Answer; divergence
34) In the Northern Hemisphere, the Coriolis effect shifts objects to the ________ of their straight-line paths. Answer; right
35) Chinook and Santa Ana winds are warm, dry winds created when air descends the leeward side of a mountain and ________ by compression. Answer; warms
36) Polar easterlies may dominate Alaska’s prevailing winds, and NE trade winds may dominate in Hawaii, but ________ dominate the prevailing winds of the “lower 48” (contiguous) United States. Answer; westerlies
37) ___________ is a situation where dense cold air actively advances into a region occupied by warmer air. Answer; cold front
38) _________ is a situation where warmer air actively advances into a region occupied by dense cold air. Answer; warm front
39) _________ is a scale for ranking how powerful a tornado is. Answer; enhanced Fujita intensity scale
40) _________ is a scale for ranking how powerful a hurricane is. Answer; Saffir-Simpson scale
26-40 Vocabulary (extra words and/or phrases are included, not all will be used)

For any Geography or History assignment, questions or homework help feel free to seek assistance from a history helper who will help handle your assignments or provide answers to your questions.

Special offer! Get 20% discount on your first order. Promo code: SAVE20