econ312 week 4 homework latest 2017 august
1. The functional distribution of income shows the distribution of income among? ______ and the personal distribution of income shows the distribution of income among? ______.
A. factors of production; job type
Elevate Your Writing with Our Free Writing Tools!
Did you know that we provide a free essay and speech generator, plagiarism checker, summarizer, paraphraser, and other writing tools for free?
Access Free Writing ToolsB. factors of production; households
C. firms and households; individuals
D. different types of workers; households according to location
E. firms; households according to age
Answer: factors of production; households
2. Indicate all the items in the following list that are not factors of production and explain why.
Item a?: Trucks used by FedEx to make deliveries
Item b?: Your dog
Item c?: Undiscovered coal reserves
Item d?: A garbage truck
Item e?: A pack of bubble gum
Item f?: The President of the United States
A. Item f because people who work in government are unproductive.
B. Item b because it isn’t productive, and item c because it isn’t available to produce goods and services. All other items in the list are factors of production.
C. Items b, c, and e because they are not productive resources used to produce goods and services land, labor, capital, or entrepreneurship.
D. Item e only because it provides personal enjoyment.
E. Items a, d, and f because they are productive resources used to produce goods and services land, labor, capital, or entrepreneurship.
Answer: Items b, c, and e because they are not productive resources used to produce goods and services land, labor, capital, or entrepreneurship.
3. Which of the following correctly lists the categories of factors of? production?
A. owners, workers, and consumers
B. machines, buildings, land, and money?
C. land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship
D. hardware, software, land, and money
E. capital, money, and labor
Answer: land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship
4. Consumption expenditure flows from ______ to ______ through the ______ markets.?
A. firms; households; factor
B. households; firms; goods
C. households and governments; firms; factor
D. governments; households; goods
E. households and governments; firms; goods
Answer: households; firms; goods
5. Tax incidence is the division of the burden of a tax between the _____ and the _____.
A. government; buyer
B.society; seller
C.buyer; seller
D. government; seller
Answer:buyer; seller
6. Despite pleas for a? freeze, stabilized rents to go up New York’s Rent Guidelines Board ignored pleas from tenants and elected officials to freeze rents for the first time in its? 40-year history and voted for increases of? 3% on? one-year leases and? 6% on? two-year leases. Maintenance costs for? rent-stabilized buildings have increased? 4%. Read the news? clip, then answer the following question. If rents for? rent-stabilized apartments are frozen while maintenance costs have? increased, ______.
A. the shortage of apartments will increase
B. the demand for apartments will decrease
C. landlords will offer more apartments for rent
D. a surplus of apartments will arise
Answer:
7. Concerned about the political fallout from rising college tuition?, the U.S. government decides to impose a price ceiling on tuition of ?$20,000 a student. If more colleges open and drive the equilibrium price of tuition to ?$15 comma 00015,000 a student?, ?_____. The market for college education is? ______.
A. a surplus of college education emerges ?; inefficient
B. a shortage of college education emerges ?; inefficient
C. a surplus of college education emerges ?; efficient
D. neither a surplus nor a shortage of college education emerges ?; efficient
E. a shortage of college education emerges?; efficient
Answer: a shortage of college education emerges?; efficient
8. A black market that emerges as the result of a price ceiling is an illegal market in which? _______.
A. the price is less than the legally imposed price ceiling
B. the price exceeds the legally imposed price ceiling
C. the quantity traded is less than the legally imposed quantity
D. the quantity traded is greater than the legally imposed quantity
Answer: the price exceeds the legally imposed price ceiling
9. If the government sets a price on dog food that is below the equilibrium? price, ______.
A. a surplus of dog food occurs
B. new firms enter the industry to meet the increase in demand that results from the decrease in price
C. existing firms in the dog food industry expand production to meet the increase in the quantity demanded
D. a shortage of dog food occurs
Answer: a shortage of dog food occurs
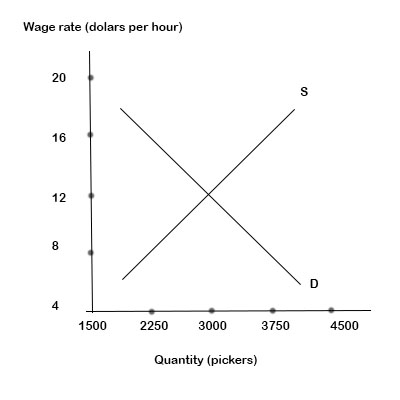
10. The graph shows the market for tomato pickers in southern California. If California introduces a minimum wage for tomato pickers of ?$8.00 an? hour, how many pickers are employed and how many are? unemployed?
Market:
The place to exchange goods and services between buyers and sellers is known as the market. Every business competes with each other in the market to attract consumers to earn profit. Every organization lies under a different market structure to engage and build a strong relationship with the customer, such as
1) Pure monopoly
2) Perfect competition.
3) Oligopoly
4) Monopolistic competition
Answer and Explanation:
Minimum wage= $16
From Demand curve
Wage rate = $16
Pickers employed = 2250
From Supply curve
Tomato pickers at wage rate $16 = 3750
11. The graph shows the market for orange pickers in Florida.. If Florida introduces a minimum wage for orange pickers of ?$14.00 an? hour, the minimum wage is? ______.
A. efficient and fair
B. inefficient but fair
C. efficient and fair only if the workers can increase the number of hours they work
D. efficient but not fair
E. inefficient and not fair
Answer:inefficient and not fair
12. The graph shows the market for blueberries. The government introduces a price support for blueberries and sets the support price at $3.003.00 a pound. _______ gain from the price support and ______ lose from the price support.?
A. Farmers; consumers and taxpayers
B. Consumers; farmers
C. Taxpayers; consumers
D. Consumers and taxpayers; farmers
E. Farmers and consumers; taxpayers
Answer: Consumers; farmers
14. The methods that governments use to support farms vary, but they almost always include all of the following except? _______.
A. the payment of a subsidy to the farms
B. the introduction of a price floor
C. lower taxes for farmers
D. isolating the domestic market from global competition
Answer: the payment of a subsidy to the farms
15. Suppose that the world price of bananas is 18 U.S. cents a pound and that when Australia does not trade bananas? internationally, the market price of bananas in Australia is 12 U.S. cents a pound. If Australia opens up to? trade, Australia? ______ bananas. The price of bananas in Australia? ______.
A. exports; falls
B. exports; rises
C. imports; falls
D. imports; rises
Answer: exports; rises
16. ______ are the ______ that we buy from people in other countries.
A. Imports; goods and services
B. Imports; goods
C. Exports; goods and services
D. Exports; goods
Answer: Imports; goods
17. National comparative advantage arises from the differences in_______ across countries.?
A. technology
B. the money cost of production
C. opportunity cost
D. population
Answer: the money cost of production
18. A country that trades internationally imports a good at a price? ______ than what domestic producers could produce the good for before the country began to trade internationally and exports a good at a price? ______ than what domestic producers could sell the good for before the country began to trade internationally.
A. higher; lower
B. lower; higher
C. lower; lower
D. higher; higher
Answer: higher; lower
19. A tariff? _______.
A. is a tax imposed on a good when it is imported
B. enables the government to satisfy the? self-interest of people who earn their incomes in? import-competing industries
C. provides revenue to the government
D. all of the above
Answer: is a tax imposed on a good when it is imported
20. Which of the following is an example of an import quota? The United States? _____ .
A. limits the quantity of textiles that U.S. producers may sell to Mexico
B. puts a 10 percent tax on auto part imports from China
C. limits the quantity of auto parts that U.S. car makers may buy from China
D. limits the quantity of sugar that farmers are permitted to produce
Answer: limits the quantity of auto parts that U.S. car makers may buy from China
21. Which of the following is an example of an export subsidy??
A. The U.S. government pays farmers? $100 per ton of sugar sold to Canada.
B. Farmers form a union to get higher prices for their exports.
C. The U.S. government pays farmers? $100 per ton of sugar produced.
D. The U.S. government buys fighter jets from Boeing.
Answer: The U.S. government pays farmers? $100 per ton of sugar produced.
22. The United States maintains an import quota on sugar. What is the argument for this import? quota???
A. Foreign producers would dump sugar at a price below its cost of production.
B. Sugar is essential for national security.
C. Foreign sugar producers pollute.
D. The U.S. sugar industry is an infant industry that will one day be able to compete without protection.
E. The import quota protects U.S. jobs
Answer: The import quota protects U.S. jobs
23. Indonesians bemoan Hollywood blockbuster blackout The Indonesian import tariff on Hollywood movies was meant? “to protect local film? makers,” but major Hollywood studios withdrew their films.? Source: The Jakarta Post?, July? 6, 2011 Indonesia is using the? ______ argument against free trade with the United States.??
A. dumping
B. lax environmental standard
C. national security
D. diversity and stability
E. infant-industry
Answer: infant-industry
24. Former Venezuelan president Hugo Chavez opposed the creation of a Free Trade Area of the Americas? (FTAA). Why? Who did he think would gain and lose? President Chavez thought that ______.?
A. Venezuela would lose tariff revenue
B. poor workers in Venezuela would lose and rich American firms would win
C. Venezuelans would lose because they would have to clean up their polluting industries
D. Venezuelans would lose because the price of oil would fall
E. Both A and B are correct
Answer: poor workers in Venezuela would lose and rich American firms would win
25. Which of the following activities is an example of dumping?
A. Dell pays a 10 percent tariff on its imports of PCs produced in China.
B. Dell exports PCs to India at a price 20 percent lower than the cost of producing them.
C. Boeing imports aircraft components because they cost less than the same components produced in the United States.
D. Boeing exports airplanes to China at a price 10 percent higher than the cost of producing them.
Answer: Dell exports PCs to India at a price 20 percent lower than the cost of producing them.
26. The fundamental force driving international trade is comparative? _______.
A. advantage: the country with the lower opportunity cost of production exports the good
B. abundance: the country that produces more than it needs exports the good
C. cost: a country trades with other countries that produce cheaper goods
D. advantage: a country exports those goods that have high prices
Answer: advantage: the country with the lower opportunity cost of production exports the good
27. With free trade between China and the United? States, the winners are? ______ and the losers are? ______.
A. U.S. consumers of U.S. imports; U.S. producers of the U.S. import good
B. U.S. producers of the U.S. export? good; U.S. consumers of U.S. imports
C. China’s consumers of China’s imports; China’s producers of its export good
D. China’s consumers of China’s export good; China’s producers of its imported good
Answer: U.S. consumers of U.S. imports; U.S. producers of the U.S. import good
28. If Korea imposes an import quota on U.S oranges, losers include Korean ______ of oranges and U.S ______ of oranges.
A. consumers; producers
B. producers; consumers
C. producers; producers
D. consumers; consumers
Answer: consumers; producers
29.The people who support restricted international trade say that? ______.
A. outsourcing sends jobs? abroad, which brings diversification and makes our economy more stable
B. U.S. firms won’t be able to compete with low-wage foreign labor if trade is free
C. protection is needed to enable U.S. firms to produce the things at which they have a comparative advantage
D. protection saves? jobs, in both the U.S. and foreign economies
Answer: U.S. firms won’t be able to compete with low-wage foreign labor if trade is free
Get more answered questions on Liberty BIBL 104 Quiz 8 – James warns believers

Special offer! Get 20% discount on your first order. Promo code: SAVE20