The Primary Chapters of a Dissertation
If you want your research work to be taken seriously by your professor or any other reader, you must follow the specific formatting guidelines. If you are a bachelor’s degree, you may be required to do a dissertation at the end of the program. Dissertations are critical for Masters and Ph.D., and you cannot afford to go wrong.
Elevate Your Writing with Our Free Writing Tools!
Did you know that we provide a free essay and speech generator, plagiarism checker, summarizer, paraphraser, and other writing tools for free?
Access Free Writing ToolsFollow the right structure to give your work credit and to present the research work you have dedicated so much time to in the best way. Understanding the main chapters of a dissertation will go a long way in helping you organize your thoughts and findings from the research.
Note that dissertation styles may vary with schools and faculties, and you should pay attention to the provided guidelines. You can also hire a professional dissertation writer to get the best scores in your dissertation paper and for guidance.
Here is a comprehensive breakdown of the primary chapters of a dissertation that will guide you on what to include in every chapter.
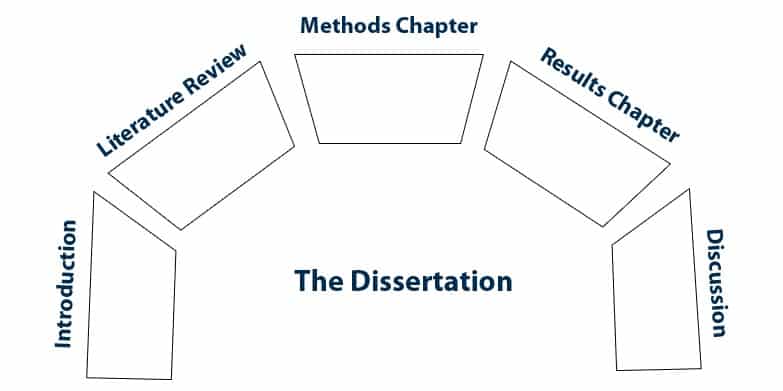
Chapter breakdown
A conventional dissertation will include:
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Methodology
- Findings
- Discussion
- Conclusion
Chapter 1: Introduction
The introduction is the first chapter of a dissertation. It should provide the background of the problem. This is the information that will bring your research work into context. This section helps the reader understand why you are focusing on this area of research or the selected topic. Remember to choose a thoughtful topic that will lay foundation for your research.
The introduction should also include the statement of the problem. Here, you are required to talk about the problem that the research is designed to address. Also, talk about the value of the study under the purpose of the study subtopic.
Research objectives and questions are also instrumental: be very specific about the research’s goals or aim. The title provides the overall goal, and the objectives are broken down further.
Chapter 2: Literature Review
The purpose of the chapter is to help you set a theoretical framework for your work. The literature review section also introduces ideas, theories, and concepts related to your area of research. It also shares your research area’s history and knowledge and shows your professor that you can understand and evaluate others’ research.
A good literature review will start with a thesis statement that will give perspective on the material. Talk about the trends that have been there in previous research on the topic, and show how your work will be an extension of prior research or will bridge existing gaps.
Show the reader how other research relates to your work and arrange your ideas logically to show the reader where you are going with the research. Also, include a conceptual framework with variables derived from the research objectives or questions.
Chapter 3: Methodology
This chapter highlights the techniques you will use to research the problem. Start with an introduction explaining the chapter’s goal and the research methods you intend to use, be it qualitative or quantitative.
Provide a justification for using questionnaires, interviews, or secondary sources for your research. You are also allowed to reference other literature when justifying your techniques.
Include the data sources and the participants of the research and highlight the technique that will be used to identify the participants. Demonstrate the steps that will be taken in conducting your research.
This chapter also talks about the methods or tools used to analyze and interpret the data.
Chapter 4: Findings
This is the chapter where your research results are presented, and all the raw data should be presented in this chapter. Start by reintroducing your research questions to bring the reader to context.
You can use a wide range of tools to present the raw data, tables, charts, graphs, and even figures. Support the tables and graphs with texts in order to take the reader through the data. Avoid interpreting data in this chapter, as that should be left out for the fifth chapter of your dissertation.
Also, only include data from your research findings and not from other researchers.
Chapter 5: Discussion
This chapter is designed to interpret the raw data and highlight the significance of the findings. In this chapter, the researcher should use the findings to answer the research questions. The researcher should also show how the results fit into the existing body of knowledge. That is the information provided in the literature review.
Show how the data met your study’s expectations, with particular attention directed to showing the relationship between the findings to your research questions. Explore the results exhaustively, backing them with the literature in chapter 2 of your research paper.
Chapter 6: Conclusion
The conclusion chapter should include the summary of the research, the conclusion, and recommendations. Summarize the key findings of your study in relation to your thesis statement. Also, talk about how the goals or objectives of the study have been met.
You can also include some of the limitations experienced during the study to guide the researchers that will explore the topic after you. Make recommendations to future researchers on the gaps that they can explore.
Highlight the research’s usefulness and how different parties can use it to address issues and improve situations.
Other elements of a dissertation
Apart from the key chapters above, there are other elements required to complete a dissertation. It should have a clear and concise title, as this will be the foundation of your research.
Include an abstract of about 300 words to give the reader an overview of what to expect from the dissertation. You should also have a table of contents to help the reader navigate your dissertation.
A list of tables and figures is also critical for easy navigation of the reader. Most importantly, have a references page. The reference page will give credit to other researchers and authors and also add credibility to your work.
It will also guide the reader on where to go if they need more information on a specific topic. Ensure that all cited sources in the text are included on the references page and arranged alphabetically.
Dissertations come with strict formatting guidelines which students must follow and understand where to start when writing your disertation paper. The guide above will help you write a well-structured dissertation that allows a chronological flow of ideas that the reader will understand.

Special offer! Get 20% discount on your first order. Promo code: SAVE20
