What is a Natural Monopoly
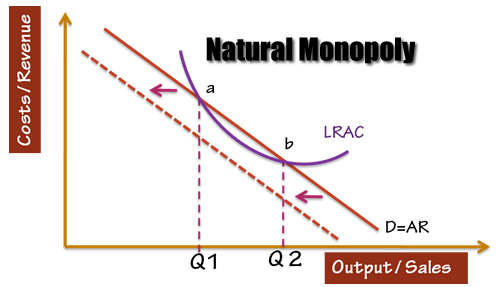
A natural monopoly is a market structure where a single seller faces the market without any significant competition. It arises when there are significant economies of scale, and increasing cost per unit of output.
Elevate Your Writing with Our Free Writing Tools!
Did you know that we provide a free essay and speech generator, plagiarism checker, summarizer, paraphraser, and other writing tools for free?
Access Free Writing ToolsCollege students often face several challenges in their academic life considering that one is required to balance between school, work and social life. To excel in school, students can seek online accounting homework help from expert tutors to aid in completing and submitting their assignments on time and boost their grades.
You can also learn some accounting tips that will help you tackle your accounting assignments better.
Characteristics of Natural Monopoly
The following are the key characteristics of a natural monopoly:
1. There is a single firm selling all goods in the market
2. Entrants into the market are unable to be economically viable
3. The firm has economies of scale
4. The average cost curves for the firm is declining
5. There is a downward sloping demand curve in the market
6 . There are no significant barriers to entry and exit from the market
Learn the types of accounting.
Pros of a Natural Monopoly
Instances where you will find a natural monopoly are where the government controls the supply of some commodities. For example ports, railways, airports, power companies, etc. The reasons why monopolies should exist in the market are:
1. Higher quality goods or services
Since there are only one or few suppliers, each supplier will give their best services in order to achieve the highest satisfaction from consumers. The monopoly supplier can also get more resources to produce better quality goods and services for consumers. Some of the reasons why this is important in the market are:
a) The monopolist can use the resources to focus on producing better quality goods and services for consumers.
b) Few suppliers would be able to get enough resources to produce better quality goods and services for consumers. This benefits consumers who can get their desired goods and services at a lower cost.
The monopoly will be more productive since there is no competition in the market forcing them to cut down their cost and produce better quality goods or services for consumers.
2. Less entry and expansion into the market
Natural monopolies are usually a threat to the entry of new firms into a market. Since there is a monopoly, there is less competition in the market allowing the monopolist to set their prices and maximize their economic profits without worrying about their competitors that could enter the market. The monopolist can also decide how many of their products or services they want to sell in the market.
3. The monopolist’s power over the market
Most natural monopolies use the monopoly power to dictate their prices or policies in their own way. The monopolist can use their discounts and other programs to entice people into buying from them. Many of the natural monopolies use this as leverage in order to influence governments into policy changes. For example, forests are vital for most industries, but when you have a monopoly on timber, you can dictate your price and even stop people from harvesting trees because you can control how much lumber is harvested.
4. Higher profits
The monopolist is able to maximize profits because they can lower the costs of production. This will attract new entrants into the market, but they only have one supplier and there are no competitors in the market. This allows the monopolist to keep their price low, which will increase their profit margins.
Cons of a Natural Monopoly
The following are the main disadvantages of a natural monopoly:
1. Slow growth rates
If there is little to no competition in the market, the monopolist can choose not to invest in research and development. This will slow down their growth rates so they won’t be able to make any profit in their company. The monopolist may also choose not to invest in new product development since they are able to maximize their profits without worrying about new entrants into the market.
2. Reliance on one supplier
The monopolist is more likely to depend on one supplier for goods and services. This can cause the monopolist to not be able to meet the demands of consumers if the company has no other suppliers. This will result in a decrease in customers for the monopolist, which can make it hard to maintain profits.
There are also no competitors in the market that could enter into the market and compete with them, which will make it hard for them to expand their way of producing goods and services since they have no competition.
3. Price discrimination
Price discrimination is the act of changing how much goods and services buyers pay (for example, it may be possible to earn higher profits when selling goods at different prices to different consumers). The main argument is that firms will try to charge different prices for the same product and will price discriminate accordingly.
The monopolist who controls the entire market will have the first right to decide how much to charge consumers. This is usually used in markets where there are few suppliers and no competition. The reason why they choose to do this is because they can earn higher profits by charging different prices to different customers.
4. Lack of innovation
This occurs because of the high budget for research and development. The monopolist is able to consider other motives, such as profit maximization rather than providing the best product for consumers. This can be bad since some monopolies will just develop a product that would be suitable for them. For example, if a monopoly company needs to pay higher taxes, they would focus on creating products that are cheaper to make so their profits aren’t affected by taxes.
Explore the pros and cons of accounting.
Natural Monopolies Examples
1. Timber
Timber is a vital wood resource. But since the government owns the forest, there will only be one supplier of lumber. The monopoly has the power to decide how much timber is harvested and sold at a lower price, which is beneficial for the consumer because they can get better quality goods and services at a lower cost.
2. Oil refining
This is another example of a natural monopoly since you only have one oil refinery in the world so there won’t be any competition in this industry for there are no other suppliers. This is beneficial for consumers since you can get your oil at a lower cost and it will be of better quality.
3. Iron
Iron is a vital resource for most industries, but there’s only one supplier of iron in the world, so there will be no competition in this industry either. Since there’s only one supplier of iron, it will make it possible to charge a higher price because they have no competition in the market. The monopolist can also choose to not produce any new iron to avoid competition and maximize profits.
4. Public utilities
Electricity, natural gas, water, and sewage systems are considered public utilities. These are considered a natural monopoly since only one company is distributing electricity or water in the market and they have no competition due to the high cost of production. The distribution of these utilities is controlled by the government in order to prevent abuse of power.
Regulation of Natural Monopolies
The following are ways that the government can regulate natural monopolies:
1. Price capping
The government can introduce price capping to ensure the monopolist is not increasing the price of goods and services too high. However, this doesn’t give the monopolist any incentive to lower costs and provide better quality goods and services since they are limited by how much they can charge.
2. limiting price increases
The government can limit price increases over a period of time so the monopolist can’t increase their profit margins too much. The government should try to regulate the way they charge consumers to prevent abuse of power.
3. Regulation of mergers
The government can enforce mergers where the company is able to buy out other companies in order to create competition in the market. However, this only happens to large corporations and not small businesses since it’s harder for them to perform research and development, which reduces their profits.
4. Breaking up monopolies
The government can choose to break up a monopoly by enforcing antitrust laws and making companies sell their assets to their competitors. This is only done when a monopoly gets too big and there are no competitors in the market, which will reduce competition.
Monopolies can be either good or bad for the market due to the lack of competition. Some monopolies are considered good since they can provide better quality goods and services at a lower cost for consumers, but others aren’t since they abuse their power and take advantage of their customers.
The government should be able to regulate monopolies in order to prevent them from abusing their power when it comes to selling goods and services.
Aditional resources;

Special offer! Get 20% discount on your first order. Promo code: SAVE20
